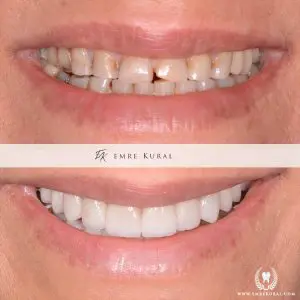
What is Smile Design?
The goal of smile design is to create artificial teeth that harmonize with a person's face, appearing natural in both shape and color.
Artificial teeth with exaggerated forms and colors that lack naturalness are easily noticeable, even by an untrained eye. Therefore, aesthetic dentistry requires meticulous preparation and planning.
Clinical and Radiological Examination
Before proceeding with aesthetic solutions, a general oral and dental examination is conducted to assess oral and dental health. A full-mouth X-ray (Panoramic X-ray) is taken to determine the course of action.
Modeling
Measurements of the upper and lower jaw are taken to create a model of the teeth and surrounding tissues. These models are then used for evaluation.
Photography
Photos of the face, smile, profile, and intraoral views are taken to capture the appearance from every angle.
Planning
Using the patient's photos and models, aesthetic issues related to the teeth and gums are analyzed in relation to the overall face. During this process, the patient is shown the problematic areas on their photos and models, and informed about possible solutions. A treatment plan is then developed to achieve the desired aesthetic outcome.
A person’s gender, age, facial structure, lips, and gum shape are all considered to create the most ideal and aesthetic smile. Factors such as the harmony between teeth and gums, gum visibility, tooth shapes, colors, inclinations, and the smile line are carefully examined. Achieving these criteria may involve gum aesthetics, teeth whitening systems, composite and ceramic laminate restorations, full ceramic restorations, implant-supported restorations, and orthodontic treatments.
Is the Harmony Between Gums and Teeth Important?
Having only white and straight teeth is not enough for a beautiful smile. Aesthetic smiles require well-arranged, healthy gums that complement the teeth and lips. In addition to being healthy, gums should also have the right color, an appropriate level of visibility in the smile line, and proper adaptation to the triangular papilla areas between teeth, without creating dark triangular gaps. The relationship between the upper and lower lips also plays a crucial role.
How Is Gum Aesthetics Achieved?
To achieve healthy and aesthetically pleasing gums, your dentist will first remove plaque and tartar buildup. If necessary, further gum treatments will be performed. Once the gums regain their health, their relationship with the teeth and lips will be evaluated, and necessary aesthetic procedures will be carried out. These procedures are usually painless and performed with devices such as lasers and electrocautery.
What Is Laminate Veneer Restoration? How Is It Applied?
Laminate veneers are thin-layer restorations applied to front teeth with poor aesthetics (such as gaps, misalignment, decay, etc.), after minimal surface preparation.
Since they are extremely thin, contain no metal, and allow light to pass through, they look almost indistinguishable from natural teeth. They are custom-made with perfect precision and adhere seamlessly to the tooth surface. In most cases, their durability and stain-resistant properties provide not only a natural appearance but also full functionality.
The application process is simple and quick. Veneers are bonded to the teeth using a special adhesive called resin cement. Once bonded, they cannot be removed and are highly resistant to breakage.
What Are Full-Ceramic Restorations?
Full-ceramic restorations are metal-free crowns made entirely of reinforced porcelain. These are preferred for their high translucency, making them more aesthetically pleasing.
Because they do not contain metal, they closely resemble natural teeth and are commonly used in the anterior (front) aesthetic region. They are an excellent choice when a tooth has significant damage due to decay, fractures, or other factors that make laminate veneers unsuitable.
Application process:
- Tooth Preparation: A 1.7-2 mm layer is removed from the entire tooth surface, painlessly.
- Impression Taking: An impression is taken, and a temporary crown is placed.
- Laboratory Work: The final ceramic crown is created in a dental laboratory.
- Fitting & Bonding: The crown is tested for fit and then permanently bonded.
Since full-ceramic restorations bond both mechanically and chemically to the tooth, they provide better retention than metal-supported restorations.
What Are Zirconium-Supported Ceramic Restorations? When Are They Used?
In aesthetic dentistry, full-ceramic restorations were introduced as an alternative to metal-supported ceramics in the front region, where achieving high aesthetics is crucial. However, full-ceramic restorations lack sufficient strength for long-span bridges in the back teeth.
To solve this issue, zirconium material was introduced as a substructure. Zirconium is a white, semi-translucent material with high aesthetic quality and superior strength. Thanks to these properties, zirconium-supported restorations have become the ideal choice for both aesthetic bridges and posterior (back) restorations.
The application process is the same as for full-ceramic restorations.
